Project Management
Risk Management Example - Strategies, the Structure and the Function
Last Updated: Jan 2025
Risk is the potential of gaining or losing something of value. Values can be gained or lost when taking risks resulting from a given action or inaction, foreseen or unforeseen. Risk combines both the uncertainty of outcomes and the utility or benefit of outcomes.
So it is very essential to have a risk management department in every institution to ensure the sustainability of the work and to develop a strategic plan to deal with the crisis and take advantage of opportunities, and at the same time maintain the human and financial resources and the rest of its assets.
What is Risk Management?
Risk management is the art of using past experience in order to reduce misfortune and avail future opportunities — in other words, a combination of techniques to obviate unintended mistakes made in the past. Along with the management of people, processes, and institutions, Risk management also is the identification, assessment, and prioritization of risks.
The department of risk management - Universities As An Example
The major aim of this department is to promote a culture of risk awareness by involving all university stakeholders in the day-to-day management of risks and encouraging university staff and students to adopt a risk management philosophy and enhancing the reputation and assets of the universities.
Classification of risks management - Universities As An Example
The table below demonstrates a number of risk categories with some examples of each.
| Category | Examples include risks relating to |
| Estates, Infrastructure & IT | • Investments in estates, infrastructure, and IT • Quality and availability of estates and infrastructure and the impact on students/staff. |
| External Relations & Partnerships | • Collaborative teaching and research with other institutions • Knowledge exchange and partnerships with industry • Other relationships with external bodies |
| Financial | • Sustainability of income streams • Budget management • Financial processes |
| Learning, Teaching & the Student Experience | • Student recruitment • New courses and programs • The student experience of the University • Learning resources and delivery |
| Organizational Development & Strategy | • The impact of internal developments and structural changes • New strategy implementation |
| Research & Innovation | • REF planning • Ethical research issues • Research funding • PGR student recruitment and support |
| Service Quality | • The quality and efficiency of administrative processes • Student and customer satisfaction |
| Staffing & Human Resources | • Staff recruitment and retention • Succession planning • Staff Management |
Risk Measurement goals
Measurement refers to the two processes of quantifying and communicating risks. This tool is vital for risk management since it provides a kind of prediction of what might happen in the future regarding the gains and losses of the firm.
Three main goals for risk measurement
Revealing the already clear risks that universities might face.
- Highlighting the risks and making them more understandable and more transparent to the people in charge.
- Anticipating the upcoming and unpredictable risks that universities might face.
For handling risk measurement, a team of experts is needed to work within a unit different and apart from the risk-taking units within the same firm.
The Universities approach risk management
- Continually classify the risks of the different operations in terms of their significance.
- Classify the risks based on the priority that is seen through their occurrences.
- Implement strategies to mitigate risks.
- Monitor the effectiveness of risk management efforts.
Four important strategies for risk management
- Avoidance: this means identifying the generator of these risks and stopping these activities in order to lessen these risks.
- Acceptance: this simply means to retain these risks (self-insurance).
- Mitigation: this means reducing the influence of these risks (loss control programs).
- Transfer: this means having a third party take responsibility for these risks (insurance).
Risk Management Protecting Universities' human, physical and financial assets
These assets can be protected by risk management through:
- Education, training, and inspection provide a real chance to prevent bad incidents.
- Having products of insurance.
- Having an administration that is responsible for claims.
- Advising senior management on how to best provide future protection against key risks in light of the university's strategic plan.
Samples of Organizational Structure (hierarchy) for Risk Management Departments
Alberta University 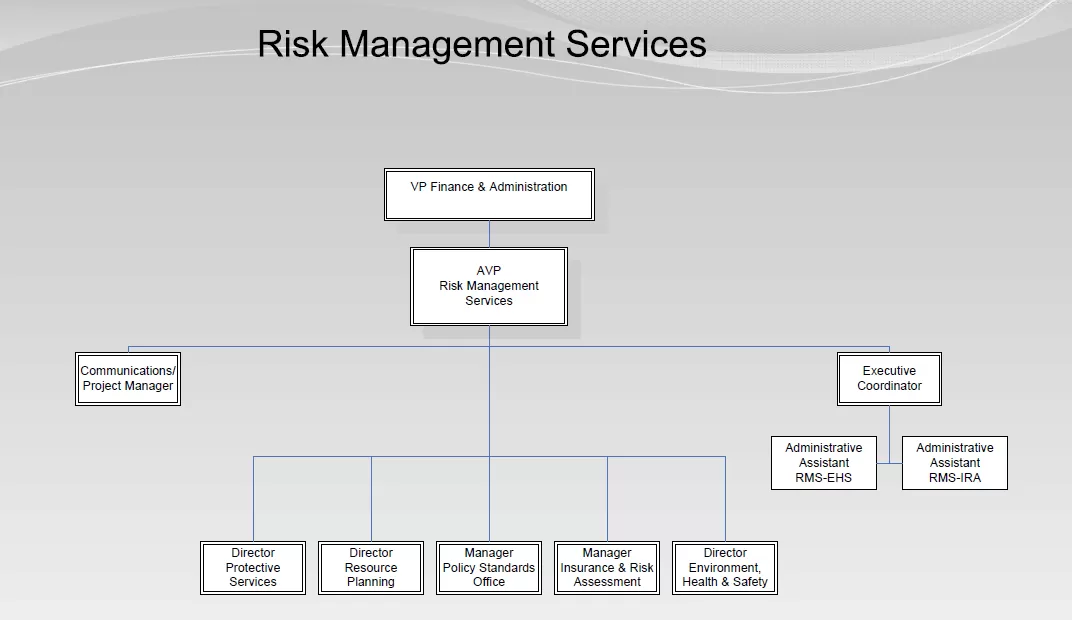
Georgetown University
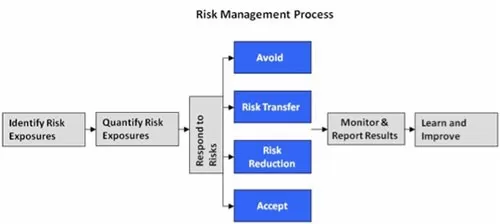
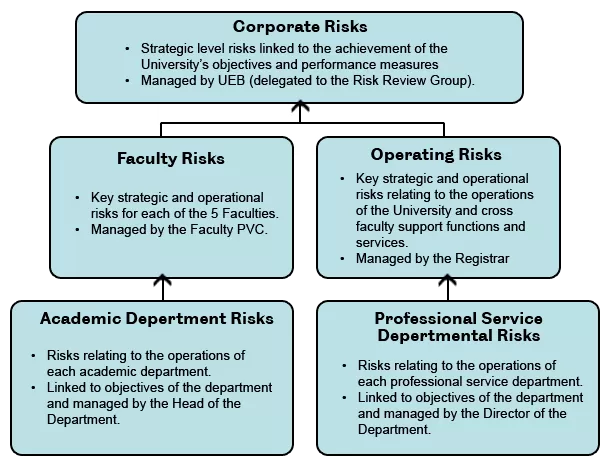
The University of Sheffield
Bakkah team for training and learning


